|
|
Big Questions in
the study of the Origins of Life
include:
How Did Life Begin ?
What are the
scientific hypotheses of the Origin of Life?
Are all life
forms related?
Are we alone in the Universe?
How do we search for Life in the Universe?

 next page next page
|
Does
the answer lie in - Basic Properties of Living
Cells...
Common traits that characteristics*
of Cells as Living entities...
1.
Cells have an Evolutionary
Origin (all
derived from an ancestral cell)NAS-1
2. Cells obey Laws of Thermodynamics -
i.e., they transform energy
NAS-2
3. Cells are Highly
Structured NAS-3 and exhibit Emergent
Properties
4.
Cells Metabolize:
possess metabolic pathways, process nutrients,
and self-adjust
to environment via metabolic regulation NAS-11
5. Cells Self-Replicate
(divide: mitosis & meiosis) NAS-15 ◄
6. Cells are Homeostatic (maintain internal constancy in
changing environs)
NAS-7
7. Cells Communicate
(signaling via
molecular & electrical charges)NAS-13
8. Cells show Animation (cyclosis-
actin protein assembly/dissasembly)
9. Cells Divide,
Grow, & Differentiate
NAS-15
10. Cells
Die - exhibit the
absence of charactistics defining life.
Let's look closer at
what each of these characteristics means...
 next panel next panel
Properties of Cells and
Life...
Our Working definition
for the basic unit of life is
the
CELL...
► "a mix of inanimate biomolecules
- selected for their fitness to carry
out
certain (cellular) biochemical functions
characteristic of life".
► "There are only
living systems: there are no living
molecules." J.
Monod-1967
1. Life
& Cells OBEY the physical/chemical LAWS of
Universe NAS-2
all living
things are parts of larger systems of matter &
energy, and
matter continually recycles as energy flows thru these
systems...
"BIOLOGICAL
LIFE TODAY IS AS MUCH A PHENOMENA OF CHEMISTRY"
and there are no unique
laws defining a Living State
separate/dintinct from
chemical/physical natural laws...
2. Cells are Highly Structured NAS-3
all living things maintain a high
degree of ORDER & COMPLEXITY.
May look diverse, yet are quite similar... (all
have membranes,
nuclei, & organelles).
the uniqueness of cells is
their structural
organization of many simple molecules
selected for their emergent properties that
helps define the living condition.
table - elements of
body* --> mixed biologically within
cells
-->
JMM
 next
panel next
panel
3. All cells are derived from a single
PRIMORDIAL cell*NAS-1
All living things are
descended from a common ancestral cell.
Let's see if we can find evidence for this
paradigm of biology.
a
Fundamental Question of Human Inquiry has been...
Where did we come from?
► What chemical
conditions may have lead to origins of life?
How did the first cells
form? What were the first living entities like?
Are we alone in the universe? From the discovery of water on Mars to
100s of exoplanets
the search for extraterrestrial life is very active.
Here are 3
possible hypotheses on ORIGIN of LIFE and a PRIMORDIAL CELL...
1. Special
Creation... benevolent entity
suspends
laws of physics &
chemistry to create life.
[not treatable by scientific method]
2. Extraterrestrial...
The Panspermia hypothesis
states that the seeds of life
exist all over the universe and can be
propagated through space to the
planets by comets and meteorites from one
location to another.
"
PANSPERMIA Animation*"...
but it may beg the question.
 next panel
(more later) next panel
(more later)
Clock Analogy
of Earth History
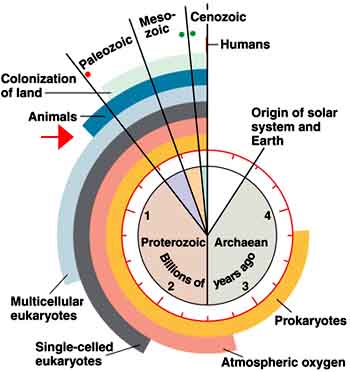
|
Geological
and Fossil Record
Formation of Earth - coalesced from space dust
|
Time scale
|
| Formation of the Earth - coalesced
from space dust |
4.5 billion years ago |
| Oldest fossil rock - 1st evidence
of life - prokaryotic like |
3.7 bya |
| 1st nucleated eukaryotic cells |
1.4 bya |
| Multicellular complex life |
0.5 bya |
| 1st humanoids ( 5 million years
ago) |
0.005 bya |
1st Homo Sapiens (between 200,000
& 300,000 ya)
|
0.0002-3 bya |
| University of Miami founded (1926) |
0.00000009 bya |
| click on the link above |
a new Geological Epoch - Anthropocene
|
|

|
a framework for reference - not for detailed
analyses
|
|
In the Beginning? What are the Common Elements for Life
and Cells* and
...
Where did the chemical
elements of Living
things come from? |
1st Molecule in
the Universe was Helium
Hydride (He-H+)... a cation of He bonded to a H.
NUCLEOSYNTHESIS - 92 natural elements
in
Periodic
Table formed by Nuclear
Fusion.
Stars made the elements* of
the Periodic Table.
|
Elements differ by numbers of protons & neutrons in their atomic
nucleus...
Creation of new atomic
nuclei comes from preexisting combo's of
protons/neutrons,
starting with H2 (1p - 92%) and He (2p - 8%) - the matter of the Big
Bang...
as Big Bang cooled fusion combined nuclei up to Li (3p),
& Be (4p), followed by Bo, C, & N.
To form heavier elements required a SUPERNOVA* (collapse of a dying star)
creating
the
intense heat & pressure needed for fusion of
protons & neutrons into new elements. |
PLANET FORMATION...
When the H2 of a
star depletes, the star dies
& ejects its mass as cosmic dust in a supernova.
Slowly microscopic dust
particles clump via
gravity and forms rocks by accretion...
Dust clouds contain common
bio molecules & are detectable today in
Interstellar Clouds*
in 2023
astrophysics document amino
acid tryptophan*
in interstellar clouds.
Dense molecular clouds undergo
gravitational
collapse forming new stars and
nearby
Planetesimals
form by accretion*
and
aggregate into PLANETS.
|
 next panel next panel
|
Earth is likely the one
planet in the Milky Way Galaxy that does
support life*
Where did
the Earth's molecular precursors of life
come from?
SPACE
DEBRIS... is the stuff of Astrobiology:
1. Tholins... a variety of carbonaceous organic compounds
formed by solar & cosmic radiation
[CO2,
CH4, ethane, in combination with N2]
have been detected in interstellar clouds*
2.
Asteroids...
rocky remnants
from birth solar system that contain molecules such as kerogen...
organic material known as
a - PAH -
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons*,
also amines & amides = some 70 amino acids,
including 8 of common 20 aa's of life,
as well as nucleobases,
quinones, & carboxylic acids... Prisitine
Asteroid Probes*
3. meteorites,
carbonaceous chondrites, are pieces of asteroids
that fall to Earth, that contain
ammonia & water and may have used heat from
gamma ray decay of AL26
to
produce amino acids as found in the Murchison Meteorite*. Early bombardment with
space dust, meteorites, asteroids, & comets
may have deposited organic molecules
on newly forming planet Earth.
4. Comets*
are mostly ice
crystals on cores of silicates & carbon. Spectral analyses
show they
contain about 20% organics
[ CO, CO2,
HCN, CH4, CH3OH,
and NH3 ]
5. Saturn's moon Enceladus*
may contain
complex organic molecules (hydrocarbons).
6. in 2023
astrobiologists document the amino
acid tryptophan* in
interstellar
clouds.
7. Mars
Missions*...
what to look
for in search for extraterrestrial
Life???
 Thus the prebiotic
chemistry may have occurred in our solar
system and elsewhere: Thus the prebiotic
chemistry may have occurred in our solar
system and elsewhere:
→ maybe
extraterrestrial amino acids built 1st proteins on Earth or in
deep space?
 next panel next panel
But, our hypothesis for the
Origins of Life postulates it may have occurred
solely on Earth...
Chemical Evolution on Earth...
a hypothesis based upon mostly circumstantial
evidence.
Space debris biomolecules initiate simple
chemical reactions capable of forming
complex molecular systems characteristic of life and
cells.
1) today's known molecules of "living cells" are made
from small number of
universal reactive chemical functional groups
[ OH,
NH3, C=O,
COOH, CH3, etc. ]
"A functional group
is a group of atom in a molecule that has
specific chemical properties"
2) these chemical
functional groups complex easily to form simple
monomers...
molecules such as -
amino acids, fatty acids, nucleotides, sugars
which are
universal to all cells...
3) these monomers easily make polymers or macromolecules [DNA,
RNA, protein]...
which favored the energy transforming
& self-replicating features,
the
so called - emergent properties that help define
today's living cells...
*
The exact
circumstances of the origin of life and the actual
nature of first molecules may
be forever lost to science, but research can at
least help us understand what is possible
because the concept of chemical evolution of life conforms
to scientific method,
and it is partly EXPERIMENTALLY TESTABLE...
.
 next panel next panel
Laboratory Experimental
Approaches to
Origins of Life Research on Earth
Ultimate Goal
could be "creation of an artificial
cell,
as a model of a life system"
Origin-of-life research has
followed 2 approaches:
1) a “metabolism first”
approach,
in which chemical cycles led to
the synthesis of complex organic molecules...
based upon hypothetical
pre-biotic chemistry, from which emergent properties
arose.
2) a “genetics first”
approach,
which favors the formation
of some sort of self replication information
molecule
being a necessary prerequisite for
life to form...
Let's look at a Metabolism 1st
Model:
Life began when
CHEMISTRY BEGAT BIOLOGY...
1922-
Oparin &
Haldane:
suggest early Earth had a strong reducing
atmosphere...
(a
reducing atmosphere is when oxidation is low -
little oxygen or other oxidizing gases)
- early
Earth = 95% steam (water vapor), with H2,
CO2, CH4, CO, N2,
SO2, H2S,
HCl, B2O3,
S, and with very little free reactive
O2
- our
current atmosphere is produced by mostly
biological systems & includes:
O2 (21%), CO2 =
412 ppm, CH4 (722 ppb
pre-industrial to 1895 ppb today), NH3 55 ppb
 next panel next panel
1953 - Stanley Miller* hypothesized that the chemistry of the
early Earth gave rise to
the organic molecules of life and tested it
experimentally. *
>
abiotic origin of organic
molecules from simple inorganic molecules
*
> H2O,
NH3, CH4, & H2
(in a reducing atmosphere) + H2S *
> in Volcanic
apparatus Miller produced HCN
and formaldehyde
which led to...
> organics* as
amino acids and
sugars *
Miller demonstrated the
plausability of spontaneous synthesis of
complex
biomolecules and thus created a new field of
science - prebiotic chemistry *
> How it might have worked on an early
Earth*
CRITICISM of
Miller-Urey research:
it wasn't fully a
reducing atmosphere, so Miller's results were
chemically unlikely;
2007, experiments redone
by J.L.Bada & S.L.Miller (March 2007) & obtained
bioorganic
molecules
in amounts comparable to those of original
Miller/Urey type experiments.
J. Bada & A. Lazcano
re-discover Miller's 1953 volcanic samples...
[Miller's Vials*]
Bada's reanalysis of the
volcanic exp's finds 23 amino acids & many
organo-compounds.
[E.T. Parker et al., NAS, Mar
2011 = DOI:
10.1073/pnas.1019191108]
[Origin of Life: An Old
Experiment Yields New Clues]Time Magazine 2011
 next
panel next
panel
Another possible process for how Chemistry begat
Biology...
B) Deep dwelling (ocean)
hydrothermal
vents*
Chemosynthesis
video*view@home
discovered
in 1977 by researchers @ Woods Hole - hot volcanic
vents on ocean floor
with minerals spewing up from
pressurized, hot springs; a source for chemical
evolution?...
these vent
areas (660oF) are full of organically rich
molecules ---> and
also
teemed with life* - including tube
worms
& thermophilic bacteria ecosystems
living in vents.
One
speculation is that life's molecules may have
originated in these hydrothermal vents,
which also may have played
a role
in?... Origin
of Cellular Metabolism.
A chemosynthetic origin
of life: via the synthesis of
organic compounds using energy
derived from
reactions involving inorganic
chemicals: Energy
in the absence of sunlight.
Gunter
Wachtershauser (German
chemist) & Claudia
Huber in papers (2003)
suggested that
life began as a synthetic chemical process via
minerals such as iron
sulfide
(FeS = pyrite), which can react with H2S and
donate e-'s (a start for energy capture
processes).
They
were able to make C-C bonds in a carbon monoxide
(Fe,Ni)S- dependent
hydrothermal environment...
maybe the beginning of a primordial metabolism...
Laboratory experimental approach to Metabolism First Metabolic
Cycle* .
Bioorganic
chemical reactivity:
may have originated
near hydrothermal vents before
genetics..
 next panel next panel
but wait, How might these
original simple biomolecules have become more complex???
Recent research suggests a role
for minerals in
Earth's Chemical Evolution of Life...
ROLE of MINERALS - minerals (as calcite, feldspar,
magnetite, clay, etc...)
may have helped fostered some
organic chemistry of early life.
1998 -
experiments begun in Robert Hazen's lab [Carnegie Institute, Washington]:
showed that amino
acids decompose at 200oC under pressure,
but when FeS (iron-sulfur)
minerals are added, amino acids remain intact.
the ROLE of
MINERALS is one of Scaffolding
Support by these minerals...
an easy way to assemble molecules in
dilute solution may be to concentrate
the molecules
on a flat
surface, which is exactly what minerals may have
allowed.
test
tube analogy
feldspar*
- a
tectosilicate mineral that houses
microscopic
pits that might have sheltered
life's precursor molecules from UV radiation and
destruction...
also would allow concentrating of components and
greater chemical reactivity
magnetite* -
(iron oxide) - triggers combining of
nitrogen & hydrogen into
ammonia (NH3), a
reduction reaction essential for organic life.
 next
next
clay* - layered
clays can trap organics
[helps concentrate
them]
between clay sheets;
held
close together molecules can then form more
complex molecules...
montmorillonite
clays
can sharply accelerate the formation of membranous
fluid-filled
sacs;
these vesicles
can grow and undergo a simple form of
division, giving them
properties
akin to primitive cells & might be a
mechanism that helped create
RNA molecules enclosed in a membrane?
The
mineral CALCITE
may provide a possible insight to a chemical
anomaly
of Life...
some molecules may exhibit chirality...
with 2 different configurations that are not
super-imposable;
i.e., configurations
that cannot be inter-converted without breaking
chemical bonds:
Requires presence of an asymmetric carbon that has
4 different groups attached [figure*].
Such
chiral molecules are optical
isomers, an known as Enantiomers*
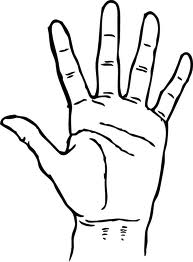 |
the anomaly of life:
the Handedness of
Life...
The emergence of biochemical homochirality was
a key step in the origin of life.
Today's cells use only 1 of 2
optical isomers, the L-form of amino acids to
make proteins,
i.e., LIFE
is HOMOCHIRAL.
Amino acids have 2
optical isomers (D & L), but
proteins contain ONLY
(L) isomers.
Cells also use only
one of the optical isomers of glucose [the
D-isomer of
D/L sugars*]. |
 next
So how did biological homochirality
originate?
next
So how did biological homochirality
originate?
Miller's experiments produces
50-50 (a racemic)
mix of the 2 isomers, equal D
& L amino acids...
the selection of
only 1 specific optical isomer [ L-amino acids ] out of 2 (D
& L) enantiomers
in the making of cellular proteins
seems improbable and must be explained in the Origins
of Life.
Some clues
might help us understand how it might have
happened:
1. meteorites - the aa's of
carbonaceous meteorites have an
enhancement of L-aa's.
in
1989 M. Engel & B, Nagy (UAz) found more L than D aa's in
Murchison meteorite.
in 2009
Glavin & Dworkin noted that isovaline had 15% L-isomer enhancement.
2. polymers
have a better a better steric fit* if they
are homochiral rather
than racemic (D&Ls).
3. G. Joyce showed in vitro one can make
a polymer of RNA with
homochiral ribose sugars,
but not so readily with a mix of D/L ribose sugars.
Could
the Earth's minerals have helped select one
isomer over the other isomer?
4. calcite*- calcium
carbonate is a mineral that
attracts D &
L - amino acids
isomers
to different crystal faces,
thus in the origin of life.
Thus one amino acid isomer could have been selected over
the other.
 next
next
Origin of Life's
Biomolecules complexity was not a single event...
more likely, it
was a gradual
sequence of modest chemical compound formations,
with an
added degree of
order & complexity of
molecular structure, selected for via molecular
evolution.
The two Earth-origin hypotheses for WHERE are: Hydrothermal vent
conditions vs. Land volcanic pools.
1. HYDROTHERMAL VENTS
- provide chemicals: Fe, S, H2S, &
energy makes a safe haven
for metabolism to evolve
and bacteria to survive. These steps include abiotic
formation of chemical
precursor building blocks, builing complex
molecular systems, eventually followed by a
"thermophilic bacteria"
(a LUCA?)
2. VOLCANIC
LANDSCAPE MODEL... [wet-dry-wet-dry
cycling model*]
This hypothesis is based on experimental evidence
that lipid-encapsulated polymers can be
synthesized by cycles of hydration and dehydration
to form protocells (encapsulated molecules).
1st step - synthesis of biomolecules (aa/na):
either via interstellar space and deposited on Earth,
or by a Miller-Urey-like mechanism...
2nd step - organic compounds in
volcanic hot springs accumulate in hydrothermal pools
where
where minerals help concentration these
biomolecules...
3rd step - polymerization* of amino acids leads
to peptide chains that fold and form enzymes?
4th step - land intertidal pools
favor lipid formations
and the possible concentration
of compounds within lipid vesicles forming complex
molecular chains
& even Protocells*
next step
- Metabolic reactions
may have been at the core of the
first living cells.
M. Ralser's work (2014) looked at metabolic
reactions that could run on their
own.
Using an Archaean ocean mimic with
metals (ferrous iron - Fe2)
described 29 non-enzymatic
reactions of the
formation/interconversion of
glucose, pyruvate, ribose-5-P, &
erythrose-4-P,
molecules common to glycolysis and
and Krebs
cycle.
 Maybe self
generating metabolic chemistry
begat the early metabolism of
Life?
Maybe self
generating metabolic chemistry
begat the early metabolism of
Life?
 next next
2nd: The "Genetics Laboratory"
experimental approach to Origins of Life research...
on the Origins of Self-Replicating
Chemical Systems...
► Self-replication... key characteristic of life: How did
self-replicating molecules as DNA evolve.
Better yet, Which came first DNA or RNA????
in 1989 Sidney
Altman and
Thomas Cech - received
Nobel Prize for
demonstarting
that RNA molecules may have CATALYTIC ACTIVITY* (Ribozymes)
i.e., these RNA's catalyze hydrolysis
(splitting) reactions of RNA phosphodiester
bonds*.
A
ribozyme with ligase
activity (linking RNA nucleotides
together) akin to artificial
RNA ligases*
could catalyze polymerization of like molecules maybe it can be
a template also,
akin to DNA -->
figure
i.e., replicate itself.
RNA molecules may have been
the 1st self replicating molecules???
1st Duplication of
RNA Molecules*
and an artificial
ribozyme RNA Polymerase*
Researchers have
been able to produce short chains of RNA, 2-40
nucleotides long. Clay minerals
do
enhance the process (chains of 50+ nucleotides
by bringing reactive molecules close together,
concentrating
them, and thereby facilitating the formation of
bonds between them).
a Ribozyme ligase scenario*
To date: No self-replicating RNA
molecules exists
naturally, but lab
experimentation
may establish that
it was feasible, and that RNA
molecules can be selected for via
Darwinian evolutionary mechanisms (natural
selection).
Ribozyme research has led to
the postulate of an RNA World...
 next panel next panel
a novel
experimental approach of Origins of Life
research... artificial
synthesis of a cell.
Synthetic Biology... construction of artificial
organisms that can reproduce & evolve.
mechanism: modify an existing
simple microbe to create a new form of single cell life.
>
J. Craig Venter, a principle investigator (P.I.) of the
Human
Genome Project
attempted
to make a new type
of bacterium using DNA manufactured in the lab;
>
using the sequenced the genes of a bacterium
called
Mycoplasma
genitalium, a gram-positive
parasitic bacterium, whose primary infection
site may be the human urogenital tract.
(M.g. causes
non-gonococcal urethritis and it is also one of the simplest known
microbes with only one chromosome and
525
genes with 476
protein-coding
genes). In 1995 Venter's group sequenced the
genome of
M. genitalium).
>
Knockout Genes... (Loss
of Function Experiments):
Venter's group began systematically inactivating
genes to determine
how many genes
are essential for life. In 1999, they
published a paper that narrowed the needs
of M. genitalium to between 265 and 350 genes
using
knockout
genes technique*.
>
a genomic goal will be to learn on a molecular
level the minimum genes
a cell needs
to thrive
and reproduce and how to artificially make those
and other genes.
To date: minimal
genomes made by knockouts in the simplest cells
show that up to
20% of genes essential for life
are of unknown function.
 next next
> New Approach:
construct an artificial or synthetic
chromosome
of the
Mycoplasma
mycoides
genome using lab-made chemicals,
& transplant it
into bacterial cell = new synthetic life form.
Venter's
group developed a strategy for
assembling viral sized pieces to produce large
DNA
molecules that
enabled them to assemble a synthetic
M. mycoides genomic chromosome
in four stages from chemically synthesized DNA
pieces averaging about 6 kb in size. This was
accomplished through
a combination of in
vitro enzymatic methods and in vivo
recombination
in yeast cells. The
whole synthetic genome (582,970 bp) was stably
grown as a yeast
plasmid.
> Next Step:
construction of a cell
completely controlled by a synthetic genome:
transplant the artificial chromosome into
a Mycoplasma capricolum
recipient cell,
which has
its own chromosome removed, creating
new cells, now called Mycoplasma mycoides*.
These new cells
are controlled only by a chemcially
synthesized chromosome.
The only DNA
in these new cells is
the designed synthetic DNA sequence, including
“watermark” sequences
and other designed gene
deletions and polymorphisms, and mutations for
protection, if cells
escape the lab. The new
cells have expected phenotypic properties and are capable
of
continuous
self-replication.
>
final steps???
new
organism created with
smallest genome of any known cellular life
form...
Craig Venter
discusses his goal for synthetic life*view@home
Building
a Minimal Cell (JCVI-syn3A) a computer simulation
model.
>
Synthetic Biology's
Potential???
Organs on a Chip*
 next next
| Summation: "simple chemical
self-assembly has lead to complex
self-replicating systems" |
|
Steps in Chemical
& Genetic Evolution of Life - "It was a Dark and Stormy Night" |
 |
 |
| 1. Abiotic
synthesis of small organic molecules |
hydrogen
cyanide & formaldehyde*
-->
makes aa's, nucleotide, lipids, etc...
|
2. Autocatalytic
assembly of polymers*
self-assembly leads to
complexity |
Condensation &
Hydrolytic Reactions*
polymer formation*
make a note*
|
3. Origin
of Heredity...
most
probably a polymer of RNA (?) |
abiotic
syntheses of RNA strands with base pairing
figure*
-->
unique polymer sequences of
RNA(?)
RNAs become polymeric
catalysts
&
show errors in replicating process
|
| 4.
Membranes probably
define First Cell |
a 1st cell may have arisen by enclosure
of a self-
replicating RNA molecules in a
phospholipid vesicle
Protobionts*
|
| 5. Translation of DNA
& RNA sequence (?) |
into
amino acid sequences?
no
experimental approaches, yet
|
"I think we’re going to have
strong indications of life beyond Earth
within a decade,
and I think we’re going to
have definitive evidence within 20 to 30
years".............
Ellen Stofan, as Director NASA
Lewis Research Center, (April 7, 2015) |
 NY cartoon
y
Origins Experimentation.
NY cartoon
y
Origins Experimentation. |
It's a long way from
research on
protobionts to a typical eukaryotic cell of today.
The evolution of
the eukaryota was single most important step in
origins
of multi-cellular life forms & was a key step
that lead to plant & animal life.
Some things that protobionts would have to develop to
become eukaryotes:
1. development of a nucleoid/nucleus
2. a
membrane to encapsulate the nucleus
3. evolve
a. a selectively permeable membrane
b. an internal cytoskeleton protein framework
c. anaerobic/aerobic cell respiration
d. various organelles: E.R., mitochondria,
Golgi, etc...
e. asexual/sexual reproductive cell cycles
These
are properties of cells where we lack much information
on their origins.
the material for exam #1
BIL 150 spring 2024 ends
here.

 <-- Study Guide <-- Study Guide
The rest
of the Top 10 attributes which we listed
that characterize cells &
Life.... [cont']
4. All cells METABOLIZE
all
life depends on chemical reactions that take place
within cells...
metabolism is chemical processes & reactivity in living
cells, where molecules
are broken down to
yield energy for vital processes & other
molecules are made.
Metabolism
is driven by energy and cells can only transform
energy via:
1. capturing light energy
( e-
),
2. redox reactions ( e-
),
& 3.
e- flow
cells extract energy from surroundings -->
as autotrophs
(light)
&
heterotrophs (food)
cells capture electrons from covalent bonds
and transfer them to other molecules
cells transform energy --> to do 'work':
osmotic, mechanical, electrical work.
cells constantly expend
energy
to maintain an ordered state away from
equilibrium.
►
AUTOTROPHS
-
organisms capable of synthesizing all their needed
organic molecules
using
CO2 as sole C source
1) photosynthetic
autotrophs... use solar photon energy of light
via e-
capture.
...capture of light is by chlorophyll,
transfers e- from
hydrogen donor (water)
to CO2
to reduce it to CH2O
2) chemotrophic -
organisms use inorganic molecules (H2S)
as their e-
energy source
► HETEROTROPHS -
obtain nutrients by dietary means: get their energy
from chemical
fuels (covalent bonds in
sugars) by oxidation;
oxidize carbs [remove e-] from CH2O
to CO2. They're able to synthesize
most, but not of their needed molecules.
 next
panel next
panel
Cells
metabolism is via Metabolic Pathways... a
synchronized system of molecular reactions
that
interact in order to carry out a specific
function; a linked sequence of individual
chemical reactions, that are regulated by a
variety of control mechanisms...
ANABOLIC - synthetic
pathway... rx's making larger from smaller
molecules -->
CO2
+ H20
----> C6H12O6
CATABOLIC -
degradatory reactions... breakdown of larger
into smaller
molecules <--
C6H12O6
----> CO2
+ H20
Metabolic
Pathways*
A
---e1---> B ---e2---> C ---e3---> D ---e4--->
E
properties: -
economy & efficiency...
- dynamic steady state... equal rates (in/out)
of intermediates
rate of synthesis = rate of degradation
Cells regulate
use of energy and respond to their environment
- control of
pathways... is via ENZYMES... and is
often a Self-Regulated process...
ex: feedback
inhibition* - negative feedbackanim -> retards activity
of pathway
- positive feedbackanim ->
enhances activity of pathway
- integration... work in a coordinated
fashion... everything at the right time
- errors can lead to
human
diseases*
 next panel another descriptor of Life
may be: carefully
orchestrated chemical reactions. next panel another descriptor of Life
may be: carefully
orchestrated chemical reactions.
5. Self-Replication (reproduction is a single most
definitive property of life)
all living things share same
genetic code, which is passed from parent to
offspring
genetic info is
in DNA
- asexuallater cell
division = MITOSIS &
- sexuallater cell
divsion = MEIOSIS
the duplication of
DNA (Replication) is
the basis of cell reproduction.
Some inanimate counterparts (or
model
systems) are useful for experimental
study...
growth of crystals in chemistry
computer
simulation models of evolutionary selection of
reproduction...
TIERRA - [digital
life
1991] is a computer model simulation of evolution
processes,
programmed by Thomas Ray
@ U. Delaware.
small
computer programs of assembly code with
directions on how to copy itself...
akin to a COMPUTER VIRUS...
These computer program compete for CPU time and
space (in memory) and are
designed to be able to mutate, evolve by selection,
combine, and self-repicate.
examples
include the AI digital simulations
as Sim City
.
Some Food for thought:
synthetic
DNA & AI
and Dose AI
want to be Alive ? ?
 next
panel next
panel
6. Osmoregulate... all life requires liquid
water (water's properties will be
covered later)
all cells regulate exchange material across cell
membrane with the environment
osmoregulation
maintains a water balance (osmolality) between
in/out
solvents
& solutes
in/out of cell are balanced by HOMEOSTASIS
(i.e., physiological mechanisms that
establish a stable equilibrium)
7. Communicate...
intra (within) &
inter (between)
individual cells
ex: chemicals/hormones/neurons = Signal Molecules
8. show Animation...
cells reveal significant 'molecular*'
& internal motion,
including cyclosis
or
cytoplasmic
streaming*
and @ molecular level:
vesicles moving along microtubules*,
also, flagella and movement of
molecules across membranes;
9. cells... all living
organisms change form & function at different
statges of their life cycles
Grow... (increase in
mass), Divide...
(increase in cell number),
Develop..., &
Differentiate... become
structurally, functionally & biochemically different
from a fertilized egg ---> to adult cells
10. Die...
the absence of the properties of life is defining
as well.
 next panel next panel
Some
Conclusions about Life, Cells, & Living
Systems...
Origins of Life is the Origin of Molecular Systems which have specific
properties...
on prebiotic Earth
massive processes of combinatorial
chemistry were going on
and
life began when one of these experiments - a
membraneous compartment of
a
specific mix of macromolecules began to grow by
energy driven polymerization
to
replicate its macromolecules; thus Origins of Life
lies in the realm of Biophysics.
Life
is manifest in the structure we call the
CELL
all cells are presumed to derive
from a single primordial cell
NAS-1
born some 3.7 billion
years ago,
√ and it out-reproduced
its contemporary competitors,
√ and today's cells
have a family resemblance
to a primordial cell...
...all use DNA
...all have same
genetic code
...all possess same basic
types of molecules
...all have similar
properties & metabolic
functions
...all use same
metabolic pathways
that define properties of life
and have a
number of unique intra-cellular parts common among
all cells.
√ a review of the
Universal properties of all cells
 next panel next panel
the definition of LIfe based upon what we've
discussed so far..
"A self-sustaining chemical system
capable of Darwinian Evolution"
a homework task to
think about*
 <-- Study Guide <-- Study Guide
back
next lecture
copyright c2023
Last update -
September 07, 2023
Charles Mallery,
Biology 150,
Department of Biology, U. of
Miami, Coral Gables, FL 33124
|