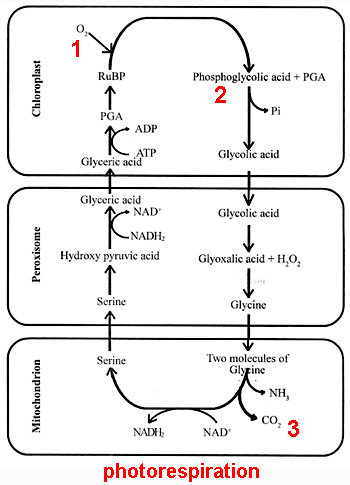
The desired reaction is the addition of carbon dioxide to RuBP (carboxylation). However, approximately 25% of reactions by RuBisCO instead add oxygen (1) to RuBP producing 3PGA and (2) 2phophoglycolate, a product that cannot be used within the Calvin-Benson cycle.
Photorespiration reduces efficiency of photosynthetic output by 25%
in C3 plants.
Photorespiration continues with a complex network of enzyme reactions that exchange metabolites between chloroplasts, leaf peroxisomes and mitochondria, eventually releasing CO2, thus the name photorespiration.
Photorespiratory carbon cycling results in around 25% of carbon fixed by photosynthesis being re-released as (3) CO2 and as ammonia. The ammonia must be detoxified at a substantial cost to the cell. Photorespiration also incurs a direct cost of 2ATP and one NADPH.
back