scroll down

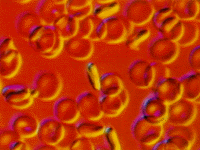
| Thalassemia, is a form of anemia quite common in the Mediterranian countries, is caused by errors in the gene splicing process. | |
 |
Normal
red blood cells contain correctly spliced
beta-globin, an important component in hemoglobin that takes up
oxygen in the lungs.
scroll down |
 |
 |
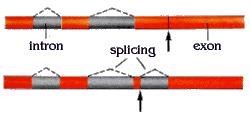
| Arrows mark 2 points of sites where point mutations causing thalassemia occur in the beta-globin gene. | |
 |
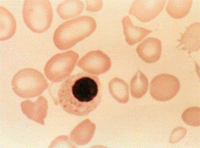
The red blood cells in thalassemia patients are distorted and sometimes immature, containing a nucleus. This is due to a point mutation in the beta-globin gene, which causes an error in splice site selection. A faulty beta-globin protein is made, leading to severe anemia. |
| back molecular genetics | Back splicing |