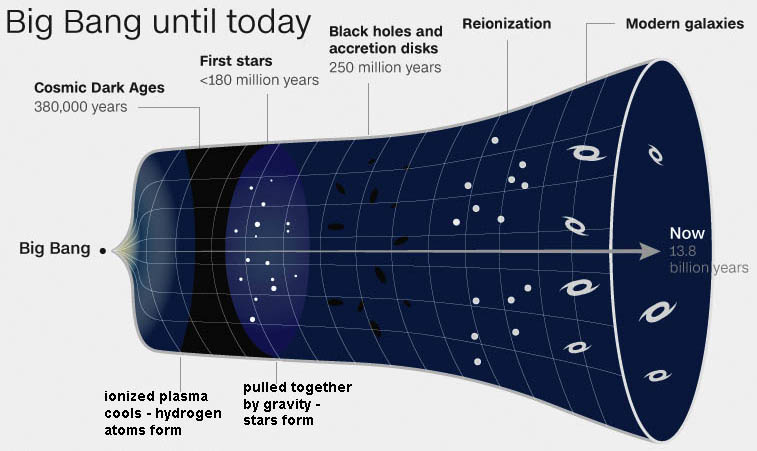
| The ages of the Universe, the Milky
Way, and Earth is the time elapsed since the Big Bang. The Milky Way is
estimated to have formed 800 million years after the Big
Band, some 13 billion years ago (bya), The Milky way is some
105,700 light years wide, is spiral shaped, and is estimated
to contain between 100 and 150 billion stars, along with
vast clouds of interstellar gases. About 8 to 11 bya the
galaxy Gaia-Enceladus merged with the Milky Way form the
current galaxy. |
A
stars brightness, temperature and elemental composition can
give age estimates when
compared with models of a stars life cycle. Researchers M. Xiang and
H. Rix at the Max Planck Institute of Astronomy
surveyed the recorded properties of some 247,000 stars in
the inner disk of the Milky
Way. They estimated that the thick core of stars around the
supermassive Black Hole, (Sagittarius A star) at the center of the
Milky Way began forming some 13bya and completed star
formation some 2 billion years later.
|
| The
age of the Universe can also be estimated using microwave background radiation that
estimates the cooling time of the Universe since the Big
Bang. Another way is to use the expansion rate of the
Universe (Hubble Constant is the rate
at which galaxies are moving away from Earth, some 73.8+2.4
Km/sec/Mpc ) by extrapolating backward in time. |
Back
Current estimates: Universe = 13.787+0.02
by Milky
Way = 13.61 by
Earth = 4.542 by
|