Because the body can not easily store ATP (and what is stored gets used up within a few
seconds), it is necessary to continually create ATP during exercise, either anaerobically or
aerobically. These pathways can be subdivided in 3 energy systems working in concert.
ATP - Adenosine Triphosphate: a complex chemical compound stored in all cells, particularly muscles.
Cells perform work from the energy released by the breakdown of this compound. Thebreakdown of ATP
produces energy and ADP.
CP - Creatine Phosphate: a chemical compound also stored in muscle, which when broken down aids in the
manufacture of ATP. The combination of ADP and CP produces ATP. ATP) stores in the muscle last only about
2-3 seconds and the re-synthesis of ATP from creatine phosphate* will continue until CP stores are depleted,
in approximately 4 to 6 seconds. This gives us around 5 to 8 seconds of total ATP production for high intensity
work (exercise) at near peak velocity.
The result of muscle contraction produces ADP which when coupled with CP regenerates ATP. CP is stored
in the muscles. Actively contracting muscles obtain ATP from glucose stored in the blood stream and the
breakdown of glycogen stored in the muscles. Exercise for longer periods requires the complete oxidation of
carbohydrates or free fatty acids in the mitochondria. The carbohydrate store will last approximately 90
minutes and the free fatty store will last several days.
2. Aneaerobic
Metabolism - Glycolysis & Lactic Acid Production
Glycolyis makes ATP via SLP and LA -
Lactic acid: Once
the CP stores are depleted the body resorts
to stored
glucose to make ATP. The breakdown of glucose or
glycogen in anaerobic conditions results in the production
of lactate and hydrogen ions. Anaerobic glycolysis
makes energy for short (less than 2 minutes)
high intensity
activity, or until lactic acid
build-up reaches a threshold with muscle
pain and fatigue occur. the lactate
threshold
or anaerobic threshold is the point where lactic acid
accumulates in blood faster than it can be removed. It
occurs at about 95% max heart rate or a [4mM]. It
signifies a shift from predominantly aerobic metabolism to
anaerobic metabolism. Athletic Training is often to
increase an athlete's lactate tolerance. Although excessive
lactate production is part of the extreme fatigue
process, it is the protons produced at the same time that restrict
further performance, thus the accumulation of hydrogen
ions is the limiting factor causing fatigue "sprint
events".
3.
Aerobic Metabolism: Endurance exercise
energy production
uses O2
via Krebs and the ETC to manufacture ATP from food mainly sugar and fat.
This system produces ATP
copiously and is the prime energy source during endurance
activities, but is slower than anaerobic energy
because it relies on the circulatory system to transport
oxygen to muscle cells to generate ATP. The aerobic
energy system is used primarily in endurance exercise (longer
than 3 minutes).
![]()
Exercise and these
energy pathways are time duration*
restricted.
| Exercise Duration | Energy Classification | Energy Supplied By | |
| 1 to 4 seconds | Anaerobic | ATP (in muscles) | |
| 4 to 10 seconds | Anaerobic | ATP + CP | |
| 10 to 45 seconds | Anaerobic | ATP + CP + Muscle glycogen | |
| 45 to 120 seconds | Anaerobic, Lactic | Muscle glycogen | |
| 120 to 240 seconds | Aerobic + Anaerobic | Muscle glycogen + lactic acid | |
| 240 to 600 seconds + | Aerobic | Muscle glycogen + fatty acids | |
| Sprint events | Endurance events | ||
Contribution of each system to ATP utilization during exercise:
All three energy systems
contribute at the start of exercise but the contribution depends upon
the individual,
the effort applied or on the rate at which energy is used.
The following graph depicts how the energy systems
contribute to the manufacture of ATP over time when
exercising at 100% effort. The thresholds (T) indicate the
point at which the energy system is exhausted - training will
improve the thresholds times.
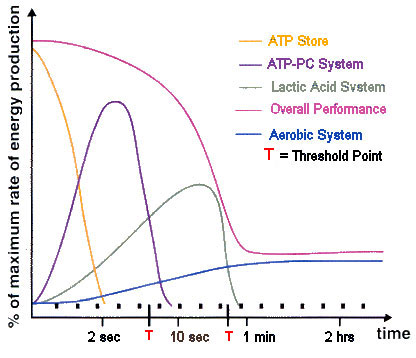
Although all energy systems turn on at the same time the recruitment of an alternative system occurs when the
current energy system is almost depleted. The following table provides an approximation of the percentage
contribution of the energy pathways in certain sports. (Fox et al. 1993)
| Sport | ATP-CP and LA % | LA-O2 | O2 |
| Golf swing | 95 | 5 | |
| Wind Sprints | 90 | 10 | |
| Field events | 90 | 10 | |
| Fencing | 90 | 10 | |
| Gymnastics | 80 | 15 | 5 |
| Volleyball | 80 | 5 | 15 |
| Tennis | 70 | 20 | 10 |
| Basketball | 60 | 20 | 20 |
| Hockey | 50 | 20 | 30 |
| Soccer | 50 | 20 | 30 |
| Skiing | 33 | 33 | 33 |
| Rowing | 20 | 30 | 50 |
| Swimming 1.5km | 10 | 20 | 70 |
| Distance running | 10 | 20 | 70 |
| Sprint Events | Endurance Events | ||
back Table adapted from Fox E. L. et al, The Physiological Basis for Exercise and Sport, 1993